How Are You Being Evaluated
This product improvement interview question is about articulating what business issues or problems you think a product has and providing ideas on how to solve them. On your own, begin by trying to figure out what the possible issues are with the product. Next, pick one problem to focus on and discuss how you would solve it. When thinking about solutions, keep in mind who the users are, what their needs are, and what the business goals are.
The interviewer is evaluating you on the following:
- Can you answer the question in a structured and organized way, or do you tend to shoot from the hip and answer without taking a moment to think about the question?
- Are you being creative and thinking outside the box for solutions?
- Are you exhaustive when talking about types of users, use cases, and solutions?
- Are you able to give detailed answers or do you tend to answer with generalizations?
- Do you articulate your answers or do you tend to ramble?
Answer Structure
Ask clarifying question to narrow the scope
If the product is a large platform with many features, ask whether there is a particular feature that needs improvement.
Summarize the product or feature
Check with the interviewer that your assumptions are correct by summarizing what the product or feature does.
Business metric to improve
If the interviewer does not tell you which business area needs improvement, you will need to come up with one. Begin by rationalizing what you think needs improvement. Then define a metric or metrics you would use to monitor and track the progress. For example, areas of improvement could be:
- Customer Base — is it too low? If yes, why? Or, could the product do better?
- Revenue — does the business need to increase the number of paid users? Or, to increase the spending amount of paid users?
- Retention — are customers churning and not returning?
- Conversion — does the business need to convert more visitors into paid users?
- User Engagement — are customers not spending time with the product?
For example, if retention is a problem, then a metric to monitor could be repeated Monthly Active Users (MAU).
Explain your approach
Give a short overview of the steps you will take to tackle the question. Explaining your method will help the interviewer understand your thought process and provides a structure for the rest of the interview.
User Goals
Describe the types of users that use the product or feature. Describe what the user’s goal or goals are when they use the product.
Use Cases
Describe use cases or situations in which users may want to use the product to achieve the goals you described. As a way to come up with use cases, create a user journey map and brainstorm actions users might want to do at each step of the journey.
How to quickly think of several use cases?
Coming up with use cases that will lead to innovative solutions is perhaps the most significant part of the product design question. Your use cases need to be detailed and insightful to uncover user needs that require better solutions.
There are various techniques to help spark ideas for good use cases. We describe some of these methods in “How would you design a bookshelf for children?”
For this interview question, we will use a user journey map and a word association technique to come up with use cases. In a feature like Yelp Home Services, where there is a distinct process from beginning to end that a user takes to get something done, a user journey map is a great tool to develop use cases. Use a journey map to define the user flow from stage to stage. Then brainstorm words or thoughts associated with each stage to trigger ideas for use cases.
Prioritize Use Cases
If there are too many use cases, pick those that seem most critical to the user’s goals.
Solutions
Describe solutions to support the selected use cases. Identify which use case each solution is solving.
Prioritize Solutions
Compare solutions based on Impact on users goals and/or business goals vs. Effort, or Impact vs. Cost. When evaluating solutions, you should aim for using a simple but effective way of selecting the best solution. Use just two to three attributes total to evaluate Impact and Effort. If you use more than three attributes, you will spend too much time evaluating solutions across attributes; and your interviewer will get bored.
Once you evaluate solutions by Impact and Effort, you may consider how innovative or risky the best solutions are. Use risk and innovation to evaluate tradeoffs between your solutions. For example, you may pick the second base solution from your Impact vs. Effort analysis because it is more innovative than the first solution.
Wireframe Solution
As a Product Manager, one of your jobs is to sketch ideas to communicate more effectively with designers and engineers. You will stand out during an interview if you provide a visual representation of your solution by sketching a wireframe. “A picture is worth a thousand words.”
Wrap up
Wrap up with key insights and provide a recommendation.
- Which solution would you recommend?
- Recap how the solution solves the problem and why it is the best.
- How would you measure the success of your recommendation?
Answer Example
Ask Clarifying Questions
INTERVIEWEE: Yelp has multiple features such as Restaurants, Nightlife, Home Services, and others. Is the goal to improve the entire platform or a specific feature?
INTERVIEWER: Let’s say we want to improve Home Services.
INTERVIEWEE: Is there are a particular aspect of the Home Services feature you want to improve?
INTERVIEWER: Well, we have seen a decrease in the number of repeat users that return to Home Services.
Best Metric to Improve
INTERVIEWEE: Okay, so you would like to improve user retention for Home Services?
INTERVIEWER: In a nutshell.
Explain Your Approach
INTERVIEWEE: Okay, if the issue is retention, the best way to improve it is by increasing the value proposition of Home Services to users. And, to do that we need to understand what their goals and key needs are that need to be fulfilled better.
Here is how I would like to tackle this question. I will start by understanding who the users of Home Services are, and what their goals or motivations are when using Home Services. Then, I will go through use cases to identify key user needs and suggest new features to increase the value of Home Services to the user.
Lastly, I will talk about metrics to validate the success of those features and make a final recommendation. How does that sound?
INTERVIEWER: Sounds good. Continue, please.
User Goals
INTERVIEWEE: The users of Yelp Home Services are probably white-collar professionals that need help with home repairs, landscaping, and other home maintenance. They are tech savvy and use the internet to search for information. When searching for professional help, they want to find the best people for the job and ideally request the service immediately. Therefore, they want to feel confident that they can trust reviews from other Yelp users, make a fast decision on a service provider, and order the service. In short, the user goal is to find and contract reliable providers fast.
With this user goal in mind, I will explore different use cases to identify a user’s need towards achieving that goal. I will create a user journey map to think about the various needs users may have at each stage of the process. Could I take a minute to list some ideas and then explain?
INTERVIEWER: Yes.
INTERVIEWEE: Okay, thanks.
Use Cases
(The interviewee uses a piece of paper or whiteboard and draws the different stages a user goes through when searching for home services providers.)
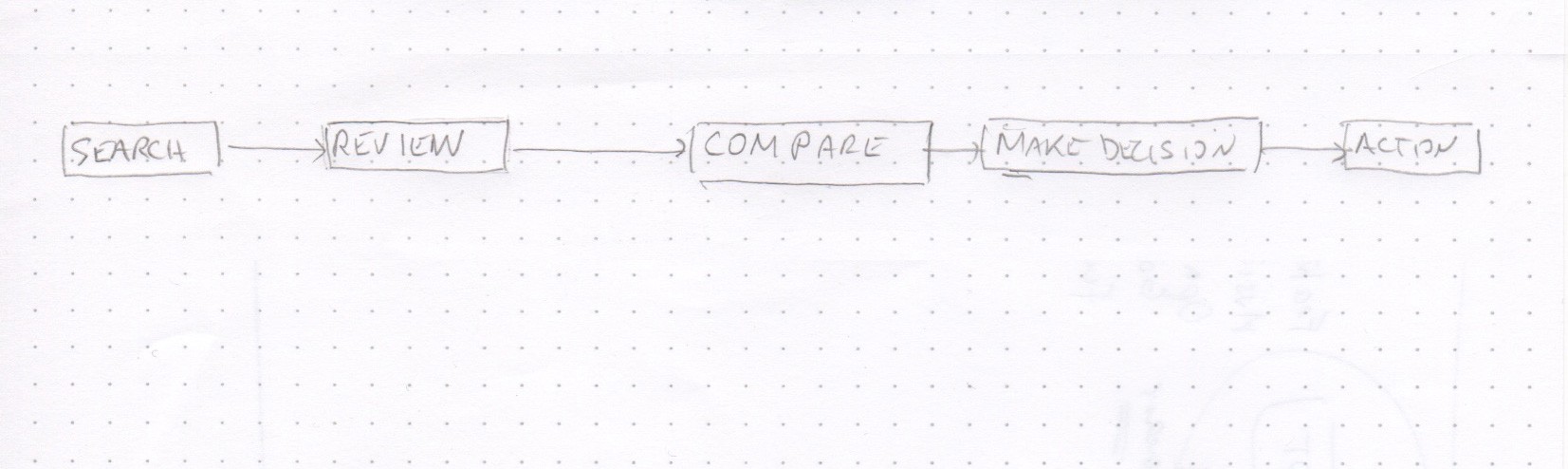
INTERVIEWEE: Here is the journey the user goes through when looking for home services:
- A user starts with a search process,
- then reviews the results,
- makes a comparison of those results,
- decides whom to contact, and finally,
- takes action such as requesting a quote, making an appointment, or scheduling a phone call.
Now, I will brainstorm activities the users may want to do at each stage, which will help frame use cases.
(The interviewee graphs a word association.)
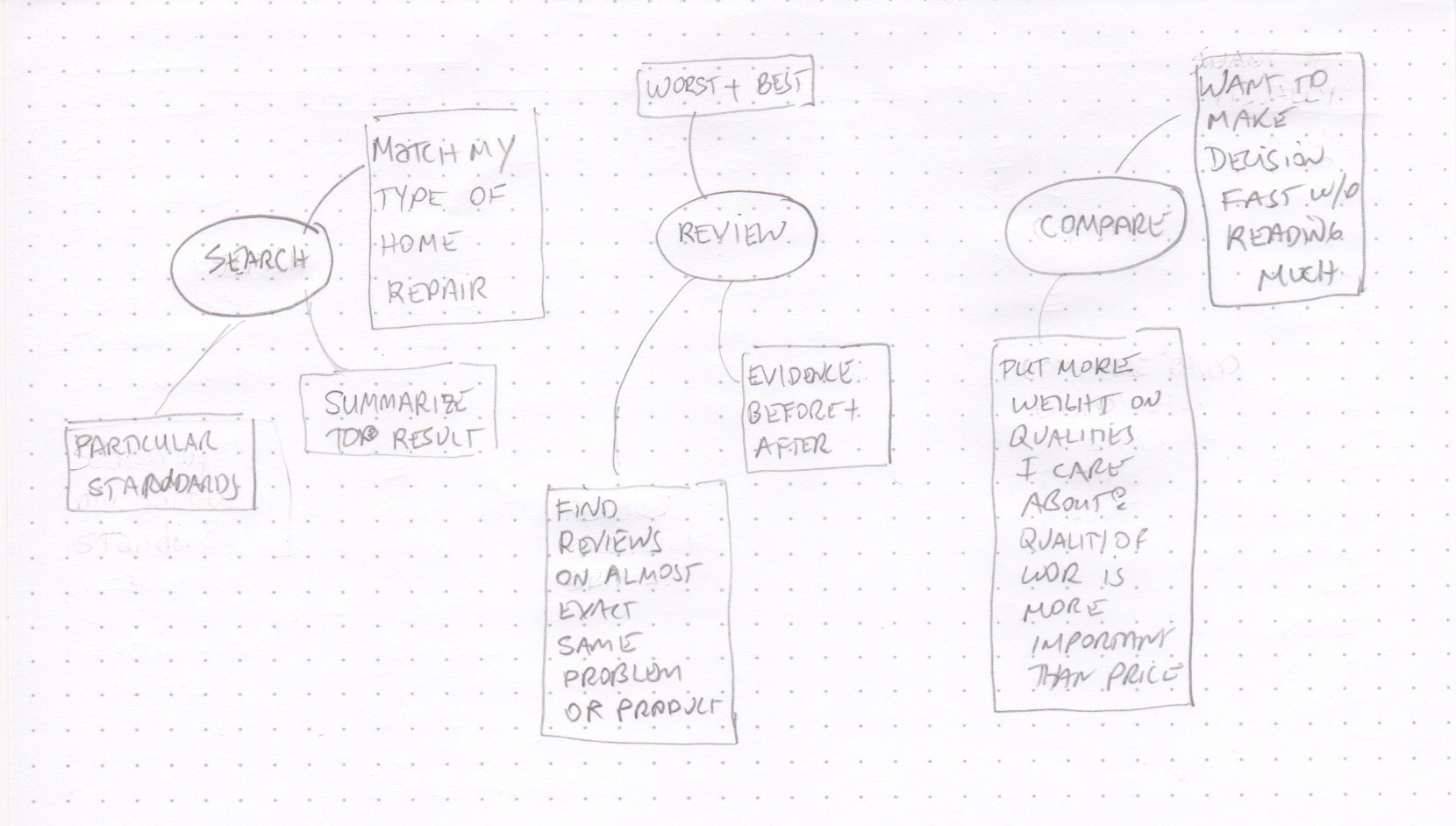
Let’s start with Search. Some thoughts users may have at this stage:
- “Which results match my type of work,”
- “I would like to see a summary of the top results,” and
- “I want to search based on my standards.”
In the Review stage, the user may think:
- “I want to see the best & worst reviews,”
- “I want to see before & after photos of work,” and
- “I want to find reviews of similar work.”
In the Comparisons stage:
- “I want to compare providers fast,” and
- “I want to rank based on my priorities.”
Okay, now I will use the word association graph to trigger ideas for use cases.
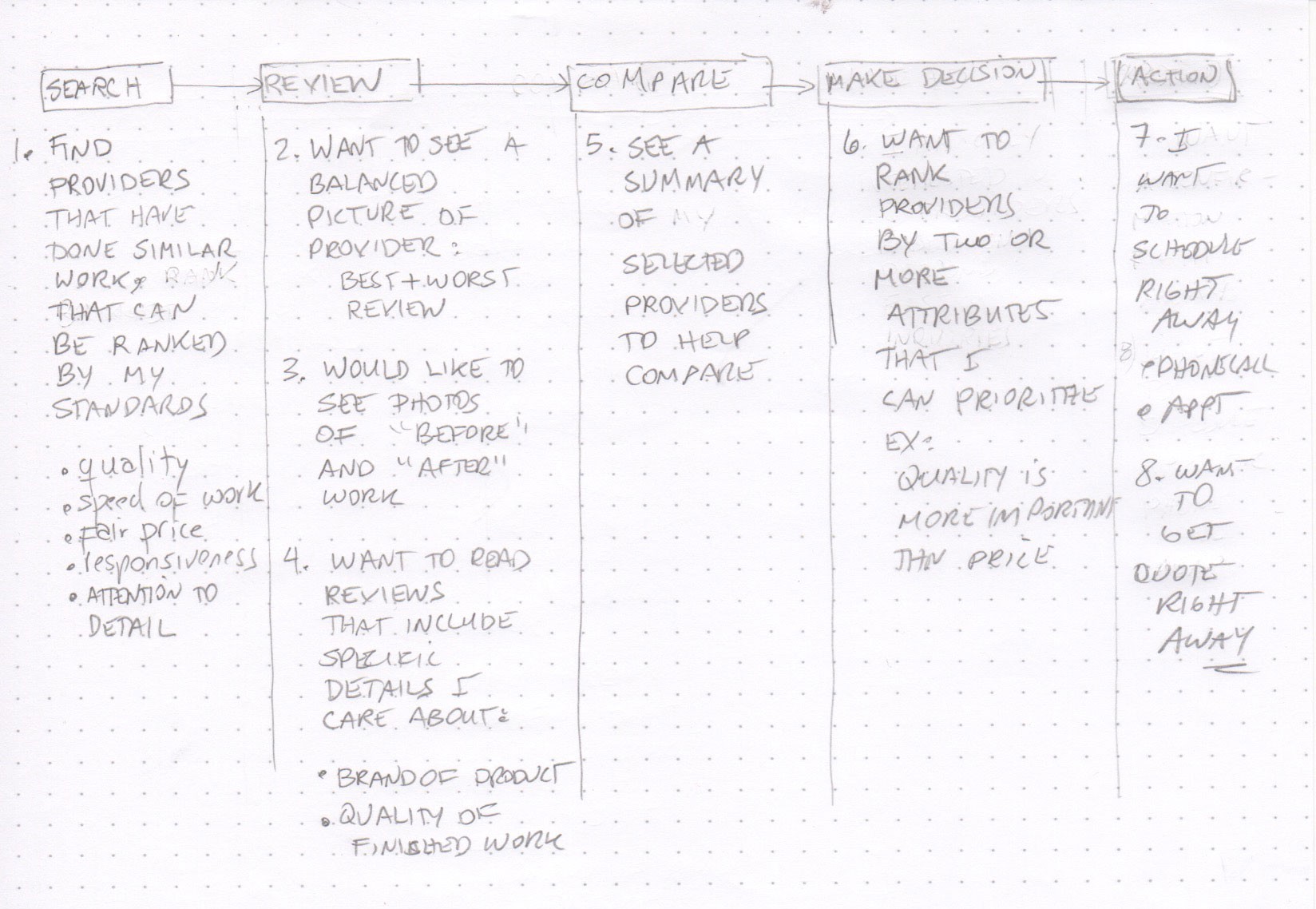
(The interviewee starts filling out the journey map with use cases, and explains at the same time.)
- (Search stage) The user wants to find providers that have done similar work and rank them by their standards, not Yelp’s default standards. These user standards can be the quality of work, the speed of work, a fair price, responsiveness, and attention to detail.
- (Review stage) The user wants to see the best and worst reviews to make an objective assessment.
- (Review stage) The user needs to see before and after photos of similar work done for other users. Seeing is believing and increases trust in reviews.
- (Review stage) The user may want to read reviews that include specific details they care about such as the quality of finished work, or the brand of the product to be replaced or fixed. This is a better-targeted approach to finding reviews that matter to the user, rather than reading review after review based on star ratings.
- (Comparison stage) The user may want to compare selected providers at once, side by side.
- (Decision stage) The user may want to put more weight on certain qualities of work to rank providers, such as placing more importance on quality than price, to make a final decision.
- (Action stage) The user may want to request a quote, make an appointment or schedule a call immediately.
Now, I would like to move on to solutions that support these use cases.
Solutions
Okay, here are some solution ideas:
- An image search feature that enables users to search for providers based on a photo of the household item that needs fixing. This feature takes care of use case 1.
- Rank results based on qualitative attributes that users care about. Use attributes like quality, the speed of work, fair price, responsiveness, and attention to detail. This feature also takes care of use case 1.
- Show a provider’s best and worst reviews side by side. Yelp prioritizes positive reviews but showing good and bad increases credibility. This feature takes care of use case 2.
- Display before and after photos provided by users, along with the price they paid. Additional information about the price will help users compare providers. This feature takes care of use case 3.
- Create tags out of words frequently used by users to describe providers and their work. The user can apply these tags to filter reviews of providers that mention these words. This feature takes care of use case 4.
- Enable users to select providers and compare them side by side. This feature takes care of use case 5.
- Let the user choose at least two qualities to sort providers by, in prioritized order. Sorting lets the user compare providers by order of conditions they care about most. For example, the user may want to sort providers by quality first and then by fast turn around. This feature takes care of use case 6.
- Use chatbots to enable users to request a quote, make an appointment or schedule a phone call. This helps users get closer to finishing the task of finding and contracting providers. This feature takes care of use case 7.
INTERVIEWER: Of all these solutions which one would you do first? Can you prioritize them?
Prioritize Solutions
INTERVIEWEE: Yes. I will prioritize the solutions across impact to the user’s goal and complexity of development. Let me go through this process using a table. The user’s goal is to find and contract reliable providers fast. And, the solutions that I think are more aligned with this goal are:
- Image search, feature (1), provides a faster search.
- Results of providers based on qualitative attributes, feature (2), provides a more reliable way for users to rank providers than only using stars.
- Before and After, feature (4), provides evidence of the quality of work, which increases reliability.
- Multi-level sorting, feature (7), makes it faster to choose the right provider because it sorts providers based on attributes that are important to the user.
- And chatbots, feature (8), provide immediate feedback to users, which helps them make tangible progress in getting the provider they want and scheduling the work.
Now, I would like to compare these solutions and select the best one.
(The interviewee talks about each entry while filling out the table.)
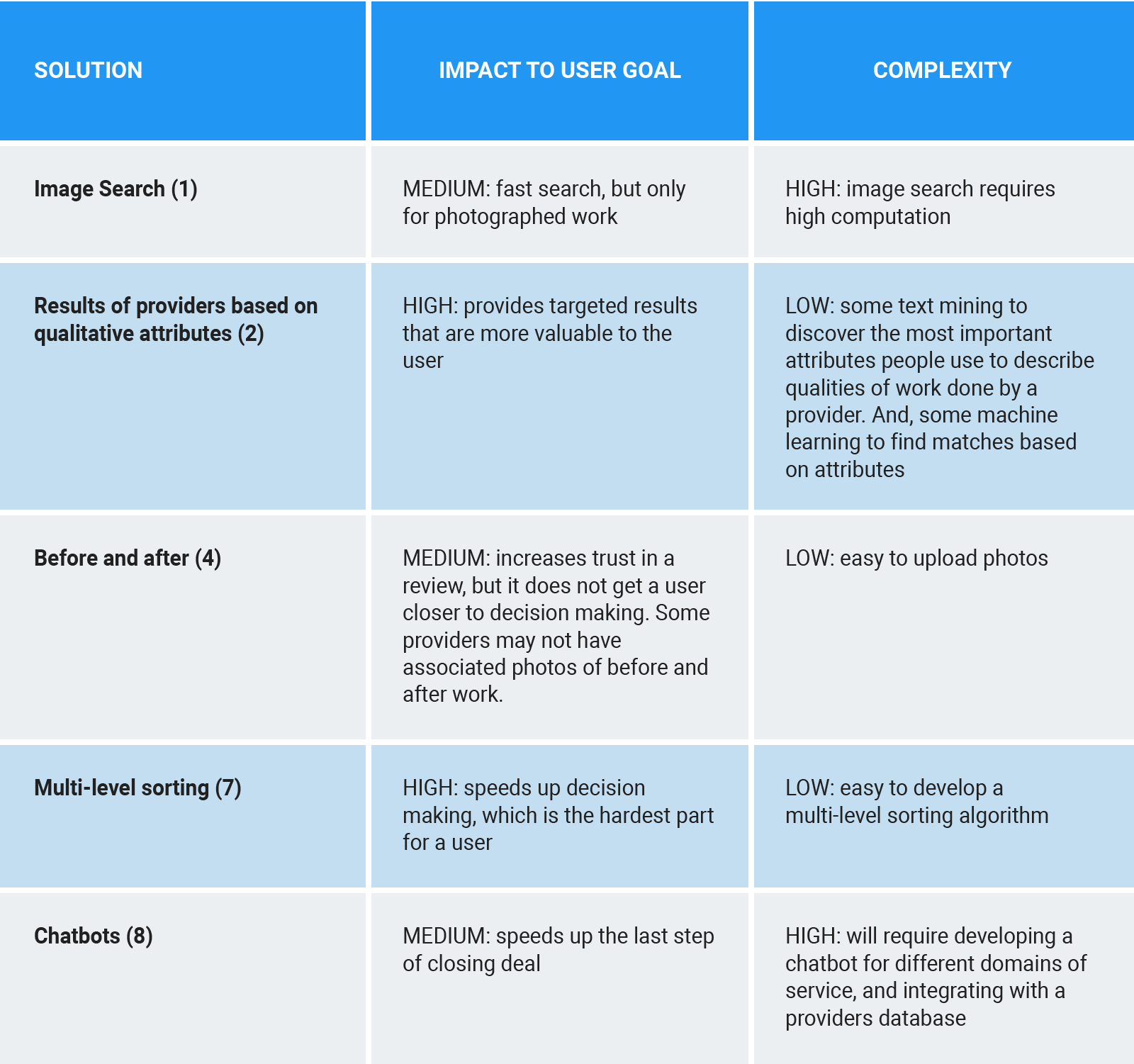
From the table, the two features that provide the highest impact for the lowest effort are Results Based on Qualitative Attributes (2) and Multi-level Sorting (7). In fact, these features go hand in hand. The user will need to specify qualitative attributes and get a first pass of results. Only after that, can the user apply multi-level sorting to rank providers based on those attributes.
Wireframe Solution
INTERVIEWEE: Would you like me to wireframe a possible solution?
INTERVIEWER: Yes.
INTERVIEWEE: Okay. May I have a minute to sketch my ideas?
INTERVIEWER: Sure.
(The interviewee takes 2 minutes to sketch a wireframe.)
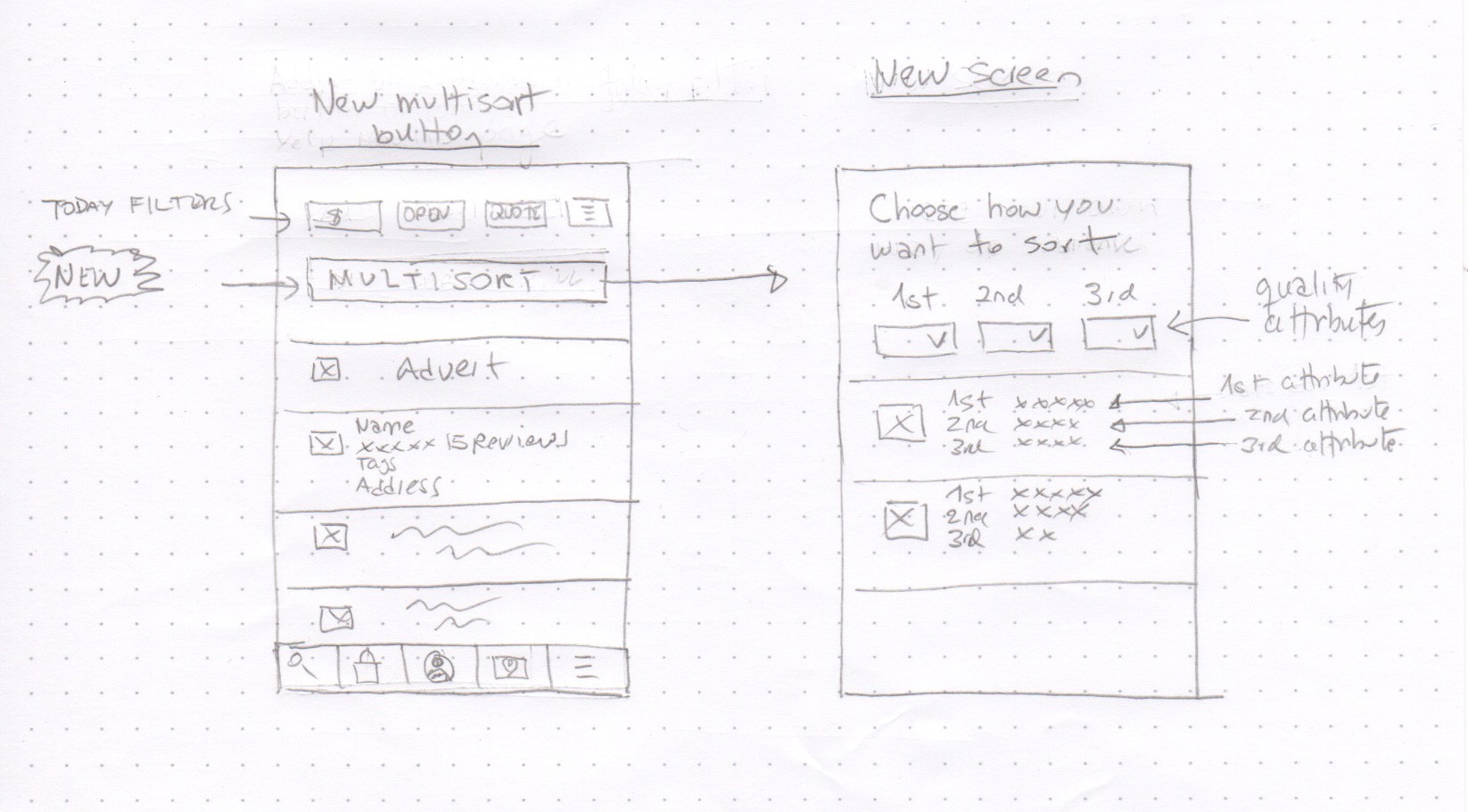
Here are two screens. The first screen is the way Yelp shows results today. It enables the user to filter results by Price, Open Now, Quote and other general filters. The presentation of results seems to favor results with the highest number of stars, and filters out results that do not match the filter values. There is no two or three level sorting system. To implement the new feature of multiple-level sorting, I suggest the following changes:
- On the first screen, after the user gets results using Yelp’s current search, display a new button to multi-sort the results.
- The new button takes the user to a second screen where they can build one, two or three level sorting based on qualitative attributes.
- The three dropdown lists enable the user to sort the results by selecting attributes they want to prioritize first, second and third.
- These attributes can be more descriptive of the service the providers offer such as the quality of work, the speed of work, fair price, responsiveness, and attention to detail. The new attributes can be obtained algorithmically, by capturing the user’s most frequently used words to describe the quality of work.
- I would limit the sorting to three levels because more than that could overwhelm the user.
Finally, to measure how successful this solution is, one key metric I would use is repeat usage of the feature per user for a period of six months to a year. I pick this timeline because home services is something that people need a few times a year. I would compare this metric between the new feature and the existing feature, which is just basic search and star ranking. And, the expectation is for this metric to be larger for the new feature.
INTERVIEWER: Okay, could you summarize your analysis?
Wrap Up
INTERVIEWEE: Sure. To increase retention I looked at how to increase Home Services value to the user. I recognized that the user’s goal is to find and contract reliable providers fast. Based on that goal, I identified user needs, and offered several solutions for them. The solution I prioritized was multi-level sorting based on qualitative attributes, because it has the highest impact on the user’s goal for the lowest effort. Although the star rating mechanism works well as a first pass for finding providers, I think users need a more qualitative way of optimizing these results. The multi-level sorting solution will provide users with a higher sense of trust in the results. And, it will also speed up their decision making. The two things they care about.
